Explain Summation in End Plate Potential
Botulinum toxin is produced by Clostridium botulinum a bacterium sometimes found in improperly canned foods. The brain is in command of the.
The two types of postsynaptic potentials are EPSP and IPSP.

. This is the time between the arrival of the action potential at the motor end-plate and the beginning of the contraction. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron. 5 BIt then disappears at about 0 mVWith further depolarization it becomes larger again but now assumes an opposite outward.
What do twitch summation and tetanus in normal muscle contraction mean. Depending on the cell and type and the nature of stimulus graded potentials that lead to action potentials are called synaptic potentials ie post-synaptic potential changes in neurons generator potentials or receptor potentials graded potentials in sensory cells causes by adequate stimuli or end-plate potentials ie synaptic. Key Difference EPSP vs IPSP.
Spatial summation is related to associating the activity of multiple inputs to a neuron with each other. EPSP stands for the Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential and IPSP stands for the Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential. Ion channels that are opened by a.
Upon stimulation by a nerve impulse the terminal releases the chemical neurotransmitter acetylcholine from synaptic vesicles. This time includes diffusion of the acetylcholine the propagation of the muscle action potential release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum etc. The summation of these IPSPs and the drop in membrane voltage will deviate away from the threshold potential inhibiting an action potential.
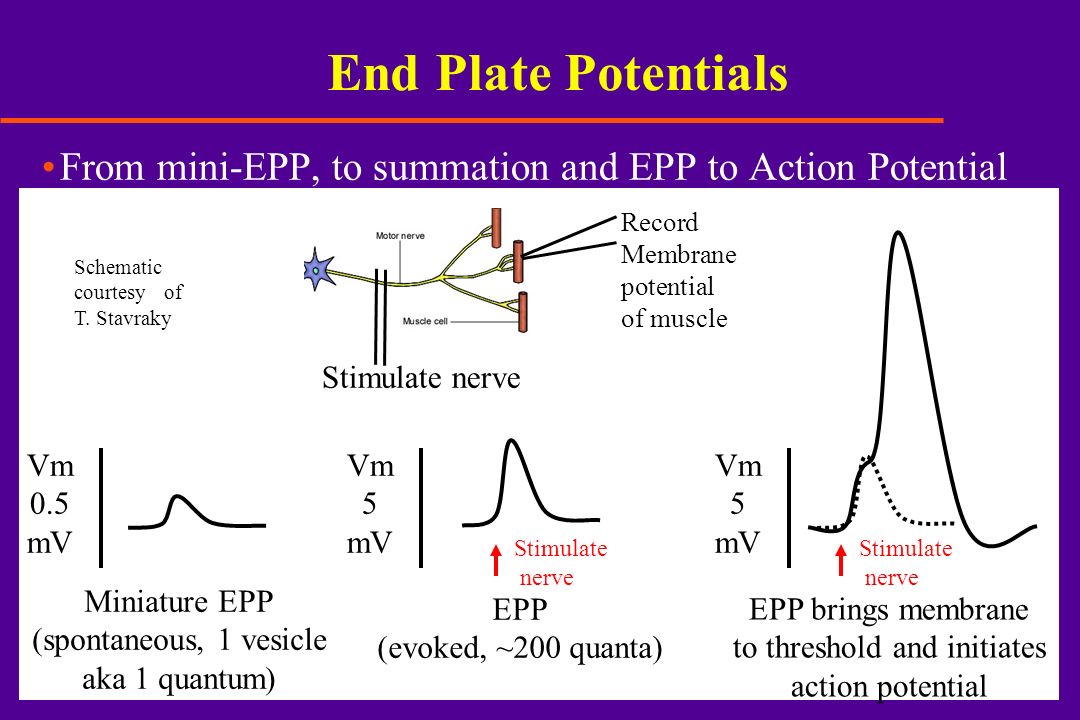
End-plate potential EPP ACh receptors are chemically gated channels that open when ACh binds to them Na diffuses into the cell through the channels while a little K diffuses out Cell membrane briefly becomes less negative at the end plate region EPP is local but it does lead to the opening of voltage-gated ion channels in the. Embedded in the end plate are thousands of receptors which are long protein molecules that form channels through the membrane. Postsynaptic potentials are changes in membrane potential that move the cell away from its resting state.
Both biological and electrochemical components are involved with the signal transmission by the nervous system. Summation may be either spatial in which signals are received from many synapses at once or temporal in which successive signals are received from the same synapse. Acetylcholine then binds to the receptors the channels open and sodium ions flow into the end plate.
This initiates the end. The different types of graded potentials are postsynaptic potentials pacemaker potentials receptor potentials end-plate potentials and slow-wave potentials. 4 At the motor end plate the action potential causes the release of packets or quanta of acetylcholine into the synaptic clefts on the surface of the muscle fiber.
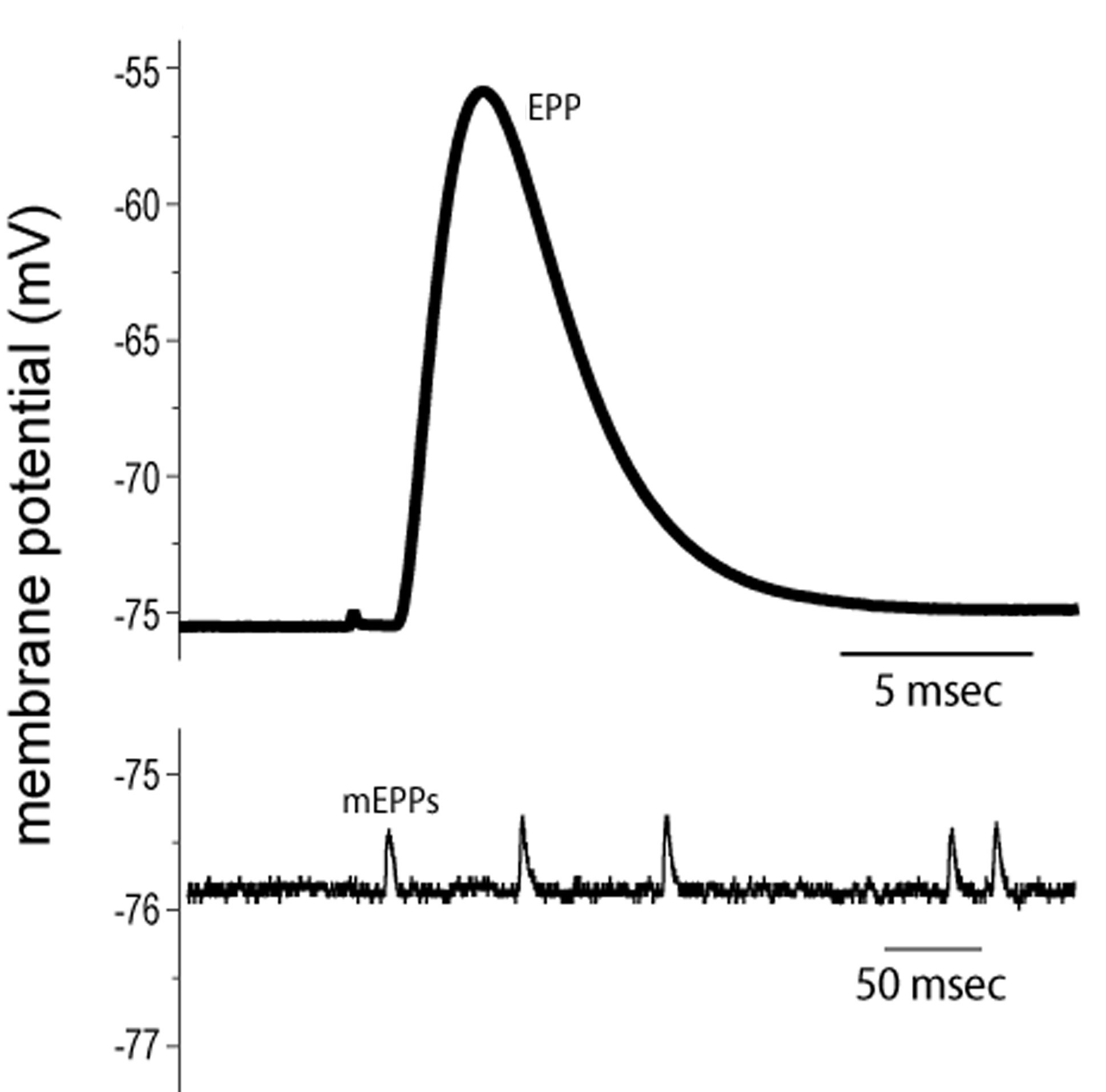
A summation of MEPPs produced by the synaptic vesicle. 5 Acetylcholine causes the electrical resting potential under the motor end plate to change and this then initiates an action potential which passes in both directions along. End plate potentials are the voltages which cause depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction.
If this end-plate poten-tial exceeds the threshold for activating Na channels an action potential results. Describe the differences in the End-Plate Potential EPP that can be generated in the neuromuscular junction NMJ of a normal and a myasthenia gravis patient in. 2 Repetitive electromyography testing involves stimulation of a nerve six to ten times at 2 to 3 Hertz.
The ionic basis for the EPSC can be examined by altering the membrane potential at which the postsynaptic membrane is being held. Thus with progressive depolarization of the holding potentials the EPSP first becomes progressively smaller Fig. Explain the importance of the motor end plates membrane potential reaching -55 mV.
An action potential is generated. Differences Between EPSP and Action Potential EPSP vs Action Potential Neuroscience has captivated the interest of many. It is a study on how the nervous system works and how the body is able to respond with different stimuli.
Building waves from muscle twitches. Has a higher threshold and stimulus voltage than nerve stimulation. With no ACh binding to its receptors at the motor end-plate no action potential is produced and muscle contraction cannot occur.
In your own words explain what an equilibrium potential for an ion is what the resting membrane potential is and how they are different. -results in the end plate potential not reaching threshold and an overall decrease in muscle contraction. Draw a zoom-in on a trigger zoneaxon and label all of the proteins required to generate an action potential.
The nervous system is important when responding to different stimuli received by the nerve cells. However these IPSPs and EPSPs may be occurring at the same time hence the postsynaptic neuron may be receiving excitatory signals from glutamate and inhibitory signals from GABA. Different potentials that build up within the nervous system components cause the transmission of different nerve stimuli.
Spatial and temporal summation can occur simultaneously. Spatial and temporal summation can act together as well. End-plate potential is produced.
Name the ion thats stored in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The equivalent of the PSP at nerve-muscle synapses is called the end-plate potential. The ACh is rapidly inactivated by acetylcholinesterase an enzyme that is manufactured by the muscle cell and.
Botulinum toxin prevents ACh from being released into the synaptic cleft. Generation of an action potential initiates the sequence of processes leading to contraction. The body itself contains chemicals which enable us to function and survive in this challenging environment.
Ingestion of very small amounts can cause botulism which. Stimulation of the muscle. They are called end plates because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large saucer-like appearance.
Draw a graph of how membrane potential changes over an action potential on a neuron. For our purposes postsynaptic potentials are measured in the dendrites and cell bodies. Temporal summation is the relationship of multiple action potentials from a single cell resulting in a significant change in the membrane potential.

Human Physiology Chapter 12 Flashcards Quizlet

Pt4 1 Neuromusc Junc Muscle Contract Williams Flashcards Quizlet

Synaptic Transmission At The Neuromuscular Junction Synaptic Transmission And The Neuromuscular Junction Medical Physiology 3rd Edition

Walk Along Theory Figure 6 7 Guyton Hall Ppt Video Online Download

Neuromuscular Junction Ppt Video Online Download

End Plate Potential Physiology Britannica

End Plate Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Today S Objective Neuromuscular Transmission Ppt Download

Endplate Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Neuro Week 4 Neuromuscular Junction Action Potentials Nerve Conduction Flashcards Quizlet

Sn18 Neuromuscular Junction And Skeletal Muscle Flashcards Quizlet

Endplate Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Endplate Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Endplate Potential All You Need To Know About Voltages That Cause Depolarization Of Skeletal Muscle Fibers Naija Super Fans



Comments
Post a Comment